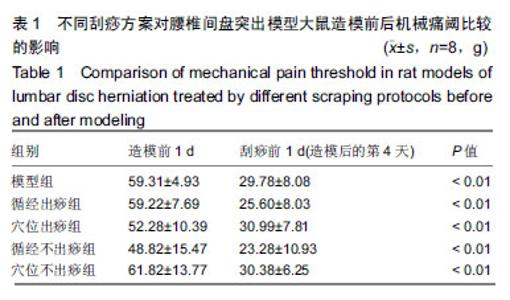
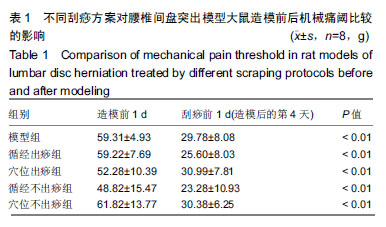
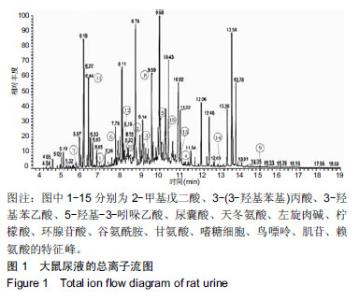
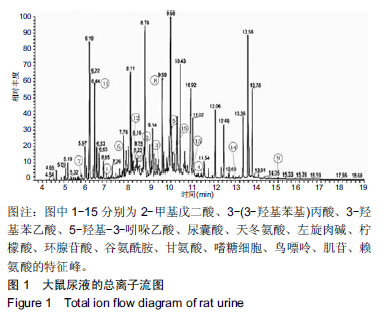
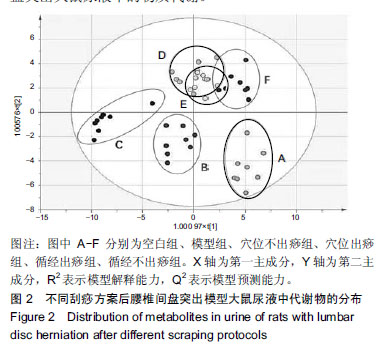
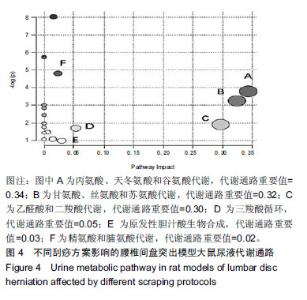
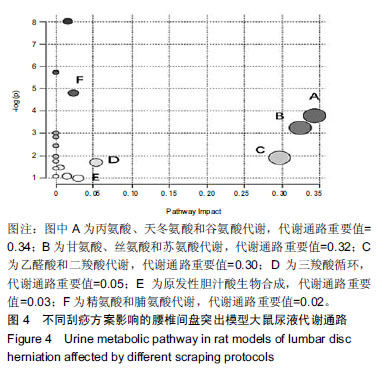
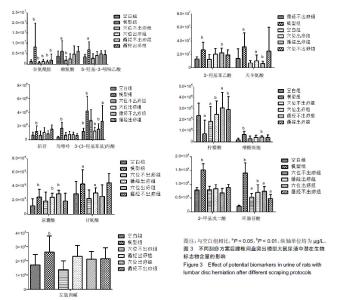
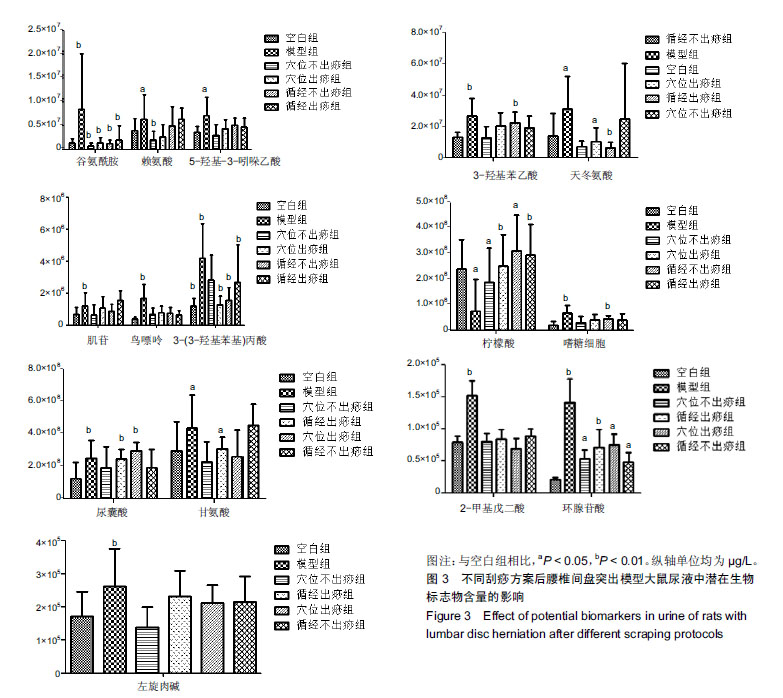
| [1]Pourahmadi MR, Taghipour M, Ebrahimi Takamjani I, et al. Motor control exercise for symptomatic lumbar disc herniation: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2016;6(9):e012426. [2]Gotecha S, Ranade D, Patil SV, et al. The role of transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic discectomy in lumbar disc herniations. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2016;7(4):217-223.[3]李林,詹红生,陈博,等.针灸治疗腰椎间盘突出症概况[J].江苏中医药, 2011,43(1):89-91.[4]曾业龙,陈东,赖美桂,等.体重指数对腰椎牵引治疗腰椎间盘突出症效果影响[J].右江民族医学院学报,2013,35(1):32-33.[5]王俊杰,杨郁文,汪丽娟,等.中医护理操作技术临床应用现状的调查分析[J].中华护理杂志,2009,44(11):1020-1022.[6]陈华,姜荣荣.刮痧疗法治疗腰椎间盘突出症理论探讨[J].长春中医药大学学报,2013,29(4):643-645.[7]司誉豪,马勇,郭杨,等.扶阳宣痹汤治疗中老年寒湿型腰椎间盘突出症临床疗效观察[J].中华中医药杂志, 2018,33(12):5726-5730.[8]林明发.推拿治疗腰椎间盘突出症的文献研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2007.[9]姜荣荣,徐桂华,陈华,等.从文献计量学角度探刮痧治疗的优势病种[J].中医学报,2014,29(5):756-758.[10]李洁,徐桂华,姜荣荣,等.刮痧法治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床疗效观察[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2013,15(5):176-178.[11]张鸿嫣.基于差异蛋白质组学研究刮痧干预腰椎间盘突出症的效应机制[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2017.[12]杨敏.基于血清蛋白质组学技术研究刮痧干预腰椎间盘突出症的效应机制[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2017.[13]赵丽云,姜会梨,任秀君,等.针刺对腰椎间盘突出症大鼠模型痛行为和脊神经根组织形态学的影响[J].北京中医药大学学报, 2014,37(8):551-555.[14]Shamji MF, Allen KD, So S, et al. Gait abnormalities and inflammatory cytokines in an autologous nucleus pulposus model of radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(7):648-654.[15]陈丽虹,岳容兆,张永怡,等.刮痧治疗腰椎间盘突出症不同方案疗效差异:基于血清代谢组学的评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(32): 5110-5116.[16]谭明生,齐英娜,姜良海,等.球囊导管构建大鼠督脉瘀阻型上颈脊髓损伤模型的研究[J].中医正骨,2016,28(12):1-5.[17]Di W, Zheng ZY, Xiao ZJ, et al. Pregabalin alleviates the nitroglycerin- induced hyperalgesia in rats. Neuroscience. 2015;284:11-17.[18]Kind T, Wohlgemuth G, Lee DY, et al. FiehnLib: mass spectral and retention index libraries for metabolomics based on quadrupole and time-of-flight gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2009;81(24):10038-10048.[19]曾佳,张弛,柏斗胜.谷氨酰胺与肿瘤[J].国际外科学杂志, 2017,44(1):48-51.[20]郭延红,杜薇,陈江,等.人参皂苷Rg1对慢性应激抑郁模型大鼠谷氨酸及其受体表达的影响[J].中国医院药学杂志, 2019,39(2):137-141.[21]宋杨,于涛,庞磊,等.HPLC法测定大鼠脑组织游离天门冬氨酸?谷氨酸?肌肽及γ-氨基丁酸[J].辽宁医学院学报, 2010,31(4):314-316.[22]Ma C, Li CX, Yi JL, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on glutamate and aspartic acid contents in the dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord in rats with neuropathic pain. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2008;33(4):250-254.[23]闫丽萍,吴辛甜,殷忠勇,等.电针对坐骨神经慢性压迫性损伤大鼠脊髓氨基酸类递质水平的影响[J].针刺研究, 2011,36(5):353-356,379.[24]郭云翮,李祥,米卫东.侧脑室注射GT-0198对坐骨神经慢性压迫性损伤大鼠的研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2018,28(25):6-10.[25]Vieira CP, De Oliveira LP, Da Ré Guerra F, et al. Glycine improves biochemical and biomechanical properties following inflammation of the achilles tendon. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2015;298(3):538-545.[26]Perego MC, Caloni F, Cortinovis C, et al. Influence of a Roundup formulation on glyphosate effects on steroidogenesis and proliferation of bovine granulosa cells in vitro. Chemosphere. 2017;188:274-279.[27]沈淑洁,水素芳,肖炳坤,等.基于1H-NMR及LC-MS技术研究金铃子散对炎症大鼠模型调节机制的影响[J].中国中药杂志, 2017,42(2):363-369.[28]Torres B, Porras G, Garcia JL, et al. Regulation of the mhp cluster responsible for 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid degradation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(30):27575-27585.[29]Arai H, Yamamoto T, Ohishi T, et al. Genetic organization and characteristics of the 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid degradation pathway of Comamonas testosteroni TA441. Microbiology. 1999;145 (Pt 10):2813-2820.[30]毛妍丽.基于代谢组学的子宫内膜异位症发病机制研究[J].中国妇幼保健,2018,33(7):1606-1609.[31]Mills E, O'Neill LA. Succinate: a metabolic signal in inflammation. Trends Cell Biol. 2014;24(5):313-320. [32]Abdel-Salam OM, Youness ER, Mohammed NA, et al. Citric acid effects on brain and liver oxidative stress in lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. J Med Food. 2014;17(5):588-598.张宁,于栋华,王宇,等.穿山龙抗急性痛风性关节炎的肾脏代谢组学研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2017,32(5):2034-2039. |